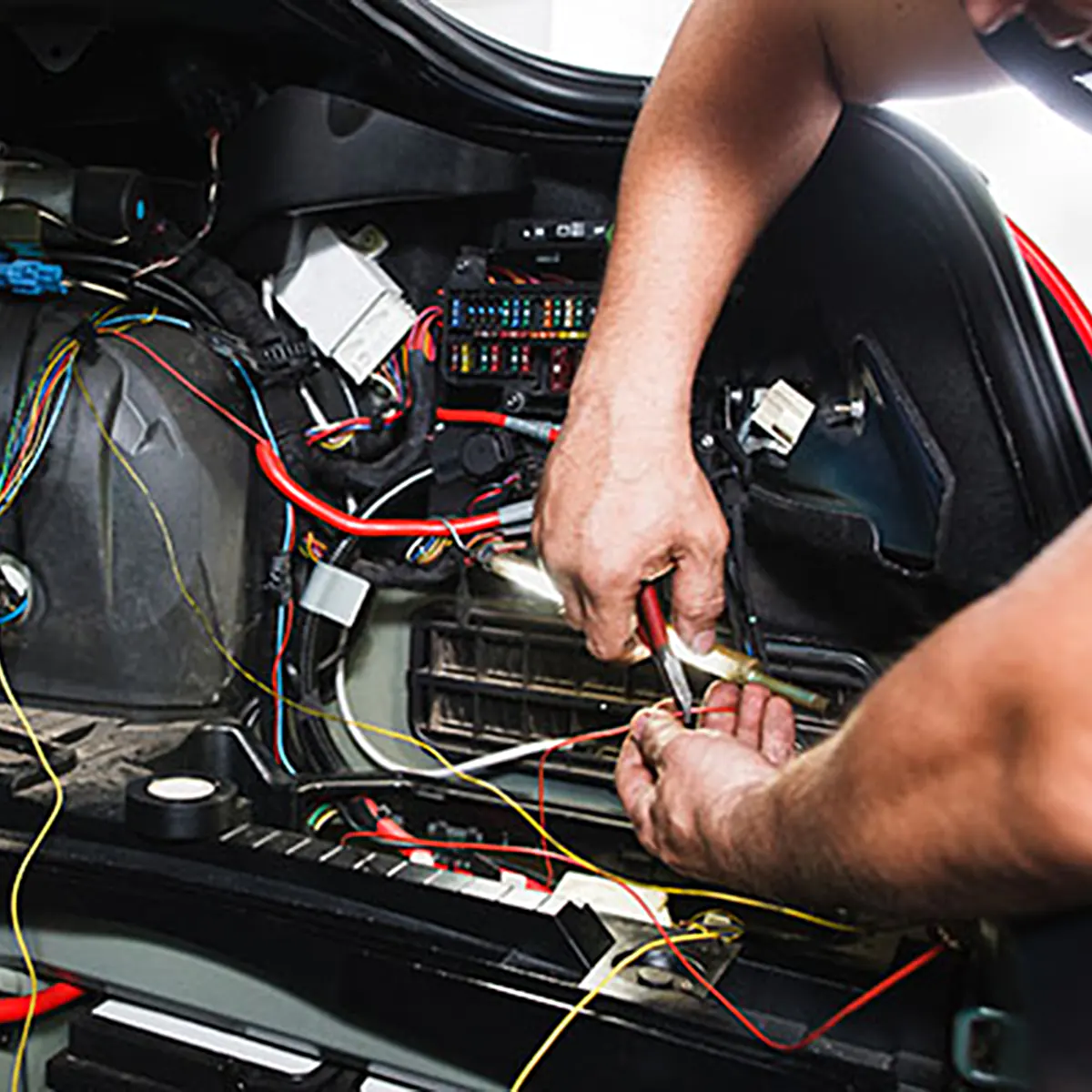
Modern vehicles are marvels of engineering, and much of their complexity comes from electrical systems that control everything from starting the engine to powering entertainment systems. While these systems improve comfort, convenience, and efficiency, they can also be sources of frustration when they malfunction. Diagnosing electrical problems in a vehicle requires patience, knowledge, and careful observation. By understanding the tell-tale symptoms of electrical issues, vehicle owners and technicians can identify problems early, prevent costly repairs, and maintain the safe operation of their vehicles.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the common symptoms of electrical problems, methods for diagnosing them, and practical strategies for repairing or mitigating issues. From dead batteries to malfunctioning sensors, we’ll cover the spectrum of electrical challenges and the signs that reveal them.
Understanding Vehicle Electrical Systems
Before diving into specific problems, it’s important to understand the role of electrical systems in vehicles. A vehicle’s electrical system is composed of numerous components that generate, store, transmit, and regulate electrical energy. These include:
- Battery: Stores energy for starting the engine and powering electrical accessories when the engine is off.
- Alternator: Charges the battery while the engine is running and provides electricity to vehicle systems.
- Starter motor: Uses battery power to turn the engine over during ignition.
- Fuses and relays: Protect circuits from overcurrent and control electrical flow to various components.
- Wiring harnesses: Networks of wires transmitting power and signals throughout the vehicle.
- Sensors and control modules: Monitor and regulate systems such as engine performance, transmission, brakes, and airbags.
Because these systems are interconnected, a fault in one component can manifest as a variety of symptoms. Understanding the interdependence of components is crucial when diagnosing electrical problems.
Common Symptoms of Electrical Problems
Electrical issues rarely present themselves as obvious, singular failures. Instead, they often show subtle signs that can indicate where the problem lies. Below are some of the most common symptoms:
1. Dim or Flickering Lights
Lights are often the first sign of electrical trouble. Headlights, brake lights, or interior lights that dim, flicker, or fail intermittently can indicate:
- Weak battery or poor charging.
- Loose or corroded battery terminals.
- Faulty alternator or voltage regulator.
- Grounding issues in the wiring harness.
2. Slow or Non-Starting Engine
Difficulty starting the engine is a classic symptom of electrical problems. Potential causes include:
- Dead or weak battery.
- Faulty starter motor or solenoid.
- Poor electrical connections.
- Malfunctioning ignition switch.
If the engine cranks slowly or not at all, checking battery voltage and connections is the first diagnostic step.
3. Frequent Blown Fuses
Fuses protect circuits from excessive current. If fuses blow frequently:
- There may be a short circuit or exposed wiring.
- A component may be drawing more current than intended.
- There could be a malfunctioning relay or control module.
Repeated fuse failures should never be ignored, as they can escalate into more serious problems.
4. Electrical Accessories Malfunction
Modern vehicles rely heavily on electrical accessories. Malfunctions can include:
- Power windows that move slowly or intermittently.
- Door locks that fail to operate.
- Infotainment or navigation systems that reboot or freeze.
- Climate control systems that behave unpredictably.
Accessory issues often point to wiring problems, bad switches, or failing control modules.
5. Warning Lights on the Dashboard
Dashboard warning lights are designed to alert the driver to system faults. Common lights related to electrical issues include:
- Battery light (charging system fault).
- Check engine light (sensor or wiring fault).
- ABS or traction control warning (sensor or module issue).
Paying attention to warning lights, even if the vehicle seems to run fine otherwise, can prevent larger failures.
6. Burning Smells or Heat from Wiring
Electrical problems sometimes manifest physically:
- A burning smell may indicate overheated wiring or a short circuit.
- Hot spots near fuses, relays, or connectors can indicate poor connections or excessive current.
These signs require immediate attention, as they pose a fire hazard.
7. Intermittent Issues
Intermittent electrical problems are among the most challenging to diagnose. They can include:
- Sporadic starting failures.
- Random accessory shutdowns.
- Flickering dashboard lights.
These often point to loose connections, corroded terminals, or damaged wiring that moves under vibration.
Tools and Techniques for Diagnosing Electrical Problems
Diagnosing electrical problems requires a combination of observation, testing, and logical reasoning. Here are essential tools and techniques:
1. Multimeter Testing
A multimeter measures voltage, current, and resistance, providing crucial information about the state of electrical components. Common tests include:
- Battery voltage: Healthy batteries typically measure 12.6 volts when off and 13.7–14.7 volts when the engine is running.
- Continuity tests: Check if wiring and fuses allow current to flow.
- Voltage drop tests: Detect excessive resistance in circuits, often caused by corrosion or loose connections.
2. Visual Inspection
Sometimes the simplest approach is the most effective. Inspect:
- Battery terminals for corrosion.
- Wiring harnesses for frayed or exposed wires.
- Fuses and relays for signs of burning or damage.
- Ground connections for tightness and cleanliness.
3. Load Testing
A battery or alternator load test simulates electrical demand, revealing weaknesses under stress that may not appear during a static voltage check.
4. Scan Tools and Diagnostic Software
Modern vehicles have complex electronic control modules. Using an OBD-II scanner or manufacturer-specific diagnostic tool can:
- Read fault codes stored in control modules.
- Monitor sensor readings in real time.
- Reset warning lights after repairs.
5. Wiggle Test
For intermittent issues, gently moving wiring harnesses while monitoring a system can reveal loose connections or broken wires hidden inside insulation.
Common Electrical Problem Sources
Knowing the likely sources of electrical faults can speed up diagnosis. Typical sources include:
- Battery Issues
Even relatively new vehicles depend on a healthy battery. Problems can include:
- Sulfation reducing battery capacity.
- Terminal corrosion impeding current flow.
- Internal shorts or open circuits in the battery itself.
- Alternator and Charging System
Alternators can fail gradually, causing voltage fluctuations and dimming lights. Symptoms include:
- Flickering headlights at idle.
- Battery light illumination.
- Unusual noises from the alternator pulley or bearings.
- Starter Motor and Ignition System
Electrical issues in starting systems often manifest as:
- Grinding or clicking noises when turning the key.
- No crank condition despite a fully charged battery.
- Occasional starting failures that are intermittent.
- Fuses, Relays, and Switches
Mechanical and electrical contacts within fuses, relays, and switches can degrade. Indicators of failure:
- Intermittent operation of accessories.
- Circuit failures with no visible damage.
- Components that operate only under specific conditions (e.g., temperature, vibration).
- Wiring Harness Problems
Over time, wires can suffer from:
- Abrasion against metal components.
- Rodent damage.
- Heat degradation.
- Poorly secured connections leading to intermittent contact.
Harness issues are a common source of intermittent and hard-to-find faults.
- Control Modules and Sensors
ECUs, ABS modules, and other control units rely on precise electrical signals. Failures can cause:
- False warning lights.
- Misbehavior of automated systems.
- Sensors sending incorrect or intermittent data.
Diagnosing module or sensor problems often requires specialized equipment and software.
Step-by-Step Approach to Diagnosing Electrical Problems
A systematic approach is the most efficient way to solve electrical issues:
Step 1: Document Symptoms
Write down all observable symptoms, including:
- When they occur (engine off, idle, driving, weather conditions).
- Frequency and duration.
- Any recent maintenance or modifications.
Step 2: Check the Battery
Start with the simplest component:
- Inspect terminals for corrosion.
- Measure voltage with a multimeter.
- Perform a load test if necessary.
Step 3: Inspect Fuses and Relays
Check all relevant fuses and relays for damage or improper function. Replace any that are suspect and test if the problem persists.
Step 4: Examine Wiring and Grounds
Visually inspect wiring harnesses, connectors, and ground points. Clean and tighten connections as needed.
Step 5: Test Charging System
Use a multimeter to measure alternator output. Ensure voltage is stable across different engine speeds.
Step 6: Use Diagnostic Tools
Scan the vehicle’s computer for error codes. Compare readings with manufacturer specifications to identify faulty sensors or modules.
Step 7: Isolate and Repair
Once the likely source is identified, isolate the component or circuit. Repair or replace as needed, ensuring all connections are secure.
Step 8: Verify Repair
After repairs, test all related systems. Monitor performance over several days to ensure intermittent issues are resolved.
Safety Tips When Working with Vehicle Electrical Systems
Working with electrical systems can be hazardous. Always follow these precautions:
- Disconnect the battery before touching major wiring or components.
- Wear protective gloves and eyewear to prevent injury from sparks or battery acid.
- Use insulated tools when working near live circuits.
- Follow manufacturer guidelines for diagnostics and repairs.
- Avoid testing high-voltage systems in hybrid or electric vehicles without specialized training.
Preventive Measures to Avoid Electrical Problems
Preventive maintenance can reduce the likelihood of electrical failures:
- Regular Battery Maintenance
- Clean terminals and check voltage periodically.
- Replace batteries before they fail completely.
- Inspect Wiring Harnesses
- Look for wear, abrasion, or rodent damage.
- Secure loose wires with clips or ties.
- Monitor Warning Lights
- Address dashboard alerts promptly to prevent escalation.
- Keep up with scheduled maintenance for sensors and modules.
- Keep Electrical Connections Clean
- Corrosion is a leading cause of electrical problems.
- Use dielectric grease on connections to prevent oxidation.
- Protect Against Water Damage
- Ensure seals and gaskets prevent water intrusion into connectors and control modules.
- Avoid washing vehicles with high-pressure water near sensitive electrical areas.
Conclusion
Diagnosing electrical problems in vehicles is both an art and a science. It requires careful observation, knowledge of vehicle systems, and systematic testing. By recognizing tell-tale symptoms such as flickering lights, intermittent failures, or unusual odors, vehicle owners and technicians can pinpoint issues before they escalate into costly repairs. Using the right tools and following a methodical approach, electrical problems—no matter how complex—can be identified and resolved efficiently.
Vehicles are becoming more dependent on electrical systems every year. A proactive approach, combined with regular maintenance, can keep these systems functioning reliably and ensure safety, performance, and peace of mind on the road. Electrical issues may be challenging, but with careful attention and proper diagnostic techniques, they can be effectively managed, keeping your vehicle operating smoothly for years to come.